스포트라이트
품질 관리 기술자, 품질 보증 검사관, QA/QC 기술자(품질 보증/품질 관리 기술자), 품질 분석가, 품질 기술자, 검사 기술자, 규정 준수 기술자, 품질 테스트 기술자, 제품 품질 기술자, 제조 품질 기술자
In one form or another, all businesses sell either products, services, or both. To become successful, these businesses must ensure their products and services meet certain quality standards. That’s why companies rely on Quality Assurance Technicians at various times throughout their activities.
For example, companies that make their own products need quality assurance (QA) reviews during the design and development phases. Models and prototypes of products are then made for further testing before they go into mass production.
Quality Assurance Technicians test products for safety and functionality, identify defects, and suggest improvements. QA checks can apply to every type of product imaginable including shoes, software programs, smartphones, vehicles, processed foods, medicines, and countless other items!
They can also provide quality control for services by developing Standard Operating Procedures, assessing training programs, gathering consumer feedback, doing audits and inspections, and analyzing performance metrics.
- Ensuring products are safe and reliable for consumers
- Playing a key role in maintaining and improving quality standards
- Opportunities to work with cutting-edge technologies and methodologies
- Collaborating with a variety of teams across different departments
근무 일정
- Quality Assurance Technicians typically work full-time, with the potential for overtime during busy periods. They may work in manufacturing plants, laboratories, or offices.
일반적인 업무
- Develop Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for quality control
- Provide training and support to production teams. Verify workers are following standards
- Conduct quality assurance reviews during the design and development phases
- Ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations
- Test models and prototypes before mass production
- Identify defects and areas for improvement. Conduct root cause analysis for defects and implement corrective measures
- Evaluate the safety and functionality of products
- Run audits and inspections of service-related processes
- Gather and analyze consumer and employee feedback to assess service quality
- Analyze performance metrics to identify areas for improvement
- Document and report quality issues and actions taken to fix them. Share reports with managers, as needed
- Monitor worker task performance and cross-check their work against applicable policies and procedural guidelines to ensure compliance
- Input data into quality management systems
- Inspect raw materials, chemical products, and other goods
- Help with applicable customer complaint investigations
추가 책임
- Assess training programs for effectiveness
- Calibrate testing equipment and tools. Perform routine maintenance
- Stay up-to-date with industry trends, Good Manufacturing Practices, and advancements in quality assurance techniques
- Maintain subject matter expertise by reviewing technical manuals, regulations, in-house policies, and other applicable guidance
- 필수 개인 보호 장비를 착용하고 안전 수칙을 준수하세요.
소프트 스킬
- 분석적 사고
- 디테일에 대한 관심
- 커뮤니케이션 기술
- Compliance orientation
- 무결성
- 관찰
- 조직
- 문제 해결
- 팀워크
- 시간 관리
- 시각화
기술 능력
- Auditing procedures
- Data and statistical analysis
- International Organization for Standardization requirements
- Knowledge of industry-specific regulations and standards
- Manufacturing processes and materials
- Quality control software and documentation
- Risk management activities
- 식스 시그마
- Standard operating procedures (SOPs)
- 기술 문서 작성 능력
- Testing and validation methods
- 농업 기업
- 자동차 산업
- Food and beverage producers
- 제조 기업
- Medical device manufacturers
- 제약 회사
- Restaurants
- Software companies
Quality Assurance Technicians are expected to find and resolve all quality-related issues with products or services. Their work is critical to ensuring that products are safe and comply with regulatory standards, and that services are meeting customer expectations.
The role requires a high level of integrity, precision, and attention to detail as even small mistakes can lead to serious problems – and potential lawsuits – if a flawed product gets mass-produced and sent to market.
Tight deadlines and production schedules can sometimes require working extra hours. Technicians may have to deal with pushback from manufacturing team members, but they must maintain their adherence to standards. They can’t ignore problems or let them slide, even if it means being the bearer of bad news!
Quality assurance is improving thanks to digital solutions like automation and AI. These advancements help to streamline inspections, increase precision, and reduce human error. In fact, AI-driven analytics can predict potential issues, allowing for preventative actions to be taken.
Technologies like blockchain enhance transparency and traceability, ensuring better real-time monitoring and consistent quality across global suppliers.
Another trend is the focus on sustainable practices and compliance with environmental regulations. Companies are adopting green quality assurance methods to reduce waste and meet the expectations of eco-conscious consumers.
Quality Assurance Technicians are often rule followers with a knack for problem-solving and a keen eye for detail. Growing up they might have enjoyed puzzles, science experiments, or activities that required precision and accuracy.
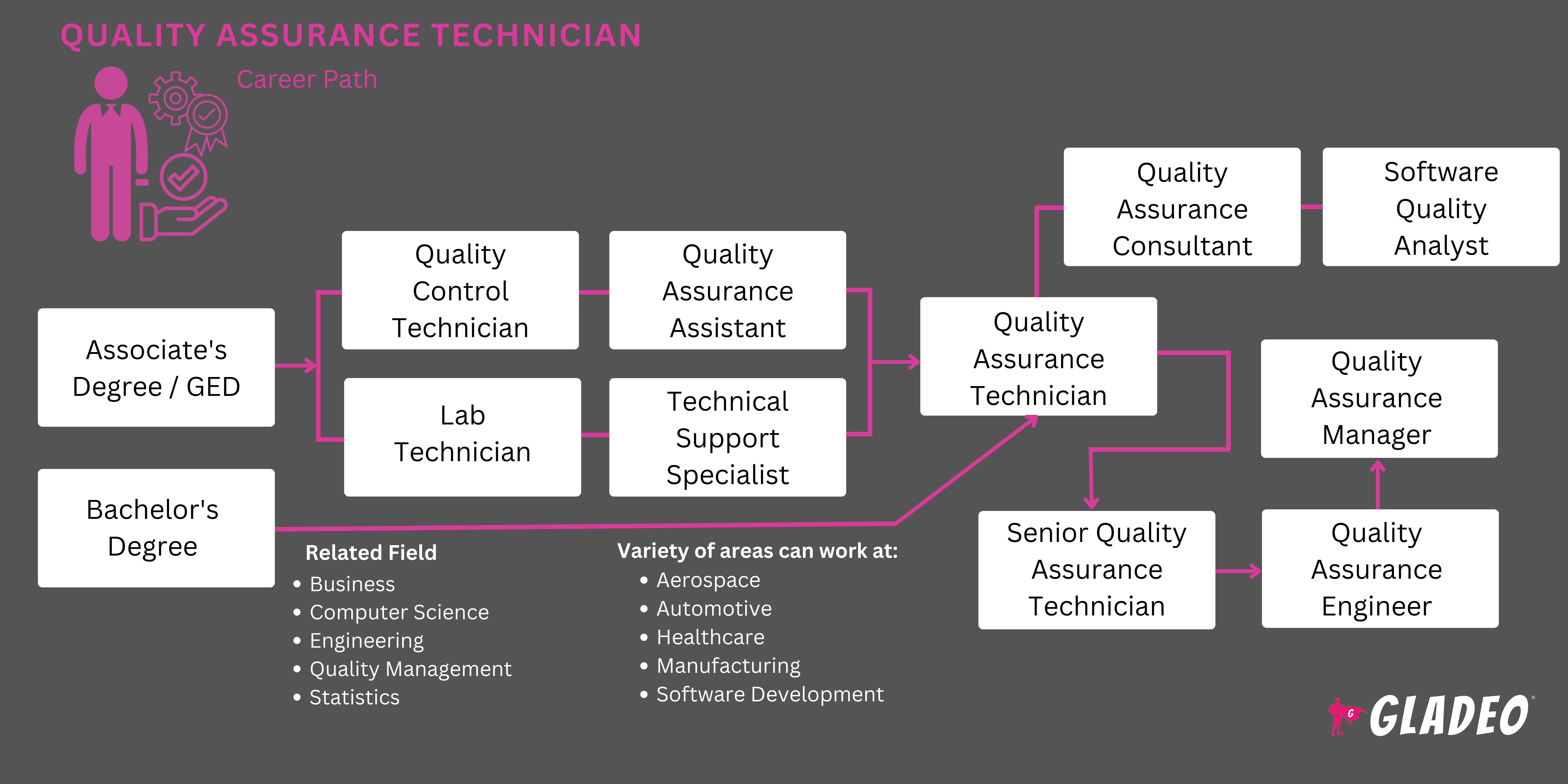
- Quality Assurance Technicians need at least a high school diploma or GED
- A college degree can be helpful, but choosing the right major will depend on the specific industry you want to work in
- Selecting an industry-specific major provides in-depth knowledge and skills tailored to that field. This can make you highly valuable to employers within that industry. However, a general quality assurance degree offers a versatile education that can be applied across various industries.
- Taking some manufacturing courses is usually beneficial no matter what you major in. Relevant courses might include:
- Manufacturing processes
- 품질 관리
- Regulatory standards
- 통계 분석
- Good Manufacturing Practices
- Some employers prefer to hire workers with years of related work experience, while others may provide on-the-job training or apprenticeships!
- 선택적 인증에는 다음이 포함됩니다:
- American Society for Quality’s Certified Quality Inspector and Certified Quality Technician
- 식스 시그마 인증
- Quality Assurance Technicians don’t necessarily need a degree, and if they do, it’s often related to the specific industry they work in. That said, some people opt for a general quality assurance degree which can apply to multiple fields.
- Ideally, programs should have seasoned faculty members and opportunities for internships or cooperative learning with local employers.
- Consider the cost of tuition, discounts, and local scholarship opportunities (in addition to federal aid).
- Decide if you want to go to college before applying for a QA job. If so, try to determine which industry you’d like to work in so you can tailor your education accordingly
- If you’re not sure, but still want to get a degree, consider a bachelor’s in quality assurance or quality management
- Try to get QA experience through part-time jobs or internships in manufacturing or quality control
- Make a portfolio of projects you’ve worked on. Keep a working resume and add to it as you gain more experience
- Study books, online articles, and video tutorials about quality assurance processes
- Review job postings in advance to learn about typical requirements, such as education, certifications, and preferred work experience
- Request to do informational interviews with Quality Assurance Technicians in different industries. Ask if you can shadow them at work for a day
- Create a list of potential job references with phone numbers and email addresses. Be sure to get permission before giving out their contact information
- Check out job portals such as Indeed, Simply Hired, Glassdoor, and Craigslist
- Look for part-time jobs, internships, apprenticeships, or anything to get your foot in the door so you can start racking up experience
- Ask working QA Technicians for job-seeking tips. Most jobs are still found through networking!
- Connect with your school’s career center for help with resumes, mock interviewing, and finding job fairs
- Check out online Quality Assurance Technician resume templates and review potential job interview questions, such as, “Can you describe a time when you identified a major defect in a product or process? How did you handle it, and what was the outcome?”
- 면접에 들어가기 전에 해당 분야에 대한 용어와 뉴스를 숙지하세요. 트렌드와 발전에 대한 인사이트에 대해 토론할 준비를 하세요.
- Know how to dress for interview success!
- Be diligent about catching issues that need to be fixed before a product goes into full production
- Talk to your supervisor about ways you can boost your knowledge and skills to serve the company better. Show your willingness to knock out extra courses or certifications like Certified Quality Technician or Six Sigma Certification
- Study manufacturer and software guides and specifications so you can be the expert on the things you’re quality control checking
- Set an example for others to follow. Mentor new workers thoroughly and make sure they understand the importance of their tasks
- Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment to avoid mishaps and hazards
- Publish articles related to your field of quality assurance to establish yourself as an industry leader
- Branch out into different types of quality assurance to expand your horizons
- Consider relocating or switching employers if necessary to advance your career!
웹 사이트
- 미국 품질 협회
- 소프트웨어 테스팅 협회
- AT*SQA
- International Organization for Standardization
- International Software Testing Qualifications Board
- National Committee for Quality Assurance
- National Quality Assurance
- QAI Global Institute
- Society of Quality Assurance
- Quality Assurance Association
- Quality Assurance International
- Quality Assurance Magazine
- Quality Digest
- Quality Magazine
도서
- Six Sigma for Dummies, by Craig Gygi
- The Certified Quality Technician Handbook, by Donald W. Benbow
- The Future of Software Quality Assurance, by Stephan Goericke
Virtually every organization needs quality assurance professionals to ensure processes are being done correctly. However, a career in QA can often involve telling other team members or stakeholders things they don’t want to hear! If you’re curious about other options, consider careers such as:
- Aircraft Structure Assembler
- Calibration Technologist
- 전기 및 전자 장비 조립업체
- Engine Assembler
- 화재 검사관
- Industrial Engineering Technician
- 산업 기계 정비사
- 물류 전문가
- Machine Feeder
- Manufacturing Technician
- Multiple Machine Tool Setter
- Process Improvement Specialist
- Production Supervisor
- 규제 업무 전문가
뉴스피드
주요 채용 정보

온라인 강좌 및 도구

연봉 기대치
New workers start around $78K. Median pay is $101K per year. Highly experienced workers can earn around $130K.






